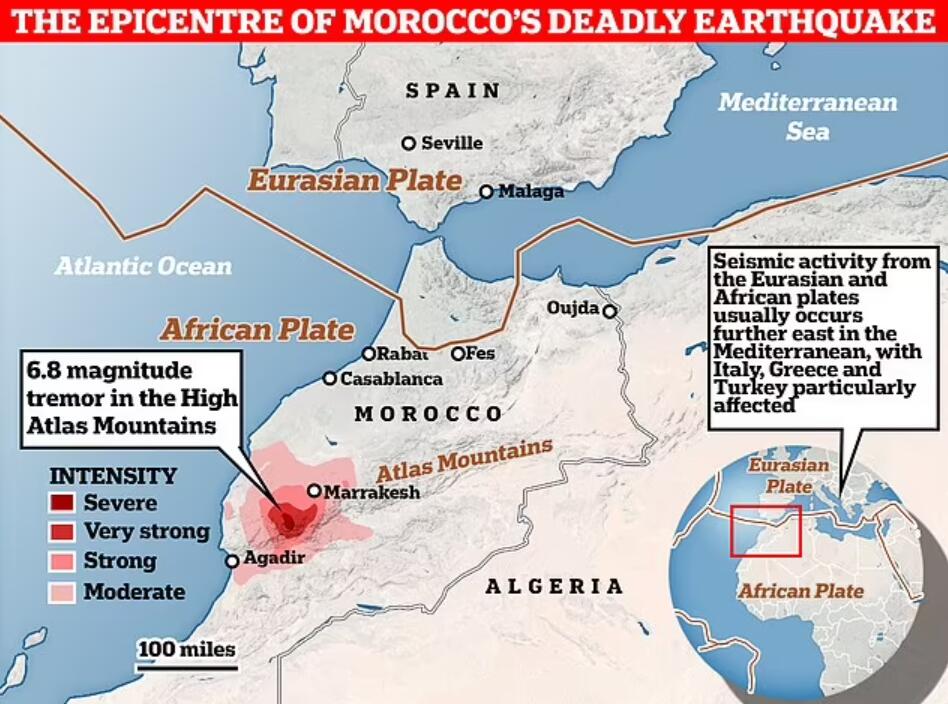
An earthquake hit Morocco on Friday and at least 2,862 people were killed in the disaster and 2,562 injured. It’s another big earthquake after the Turkey earthquake on Feb 6th,2023. The Morocco earthquake epicenter was located in the High Atlas mountain range, about 72 kilometers (44.7 miles) southwest of Marrakech.
Why earthquake strike Marocco?
Earthquakes occur in Morocco due to its location at the intersection of several tectonic plate boundaries and geological features that make it prone to seismic activity. Here are the main reasons why earthquakes happen in Morocco:
Morocco is located at Tectonic Plate Boundaries
Morocco is located at the convergence of several major tectonic plates, including the Eurasian Plate, the African Plate, and the Atlantic Plate. The interactions between these plates and their boundaries are where most earthquakes occur due to the movement and stress generated by plate motions.
Atlas Mountains
The Atlas Mountains run through Morocco and are the result of the collision between the African Plate and the Eurasian Plate. The intense geological forces associated with this collision contribute to seismic activity in the region.
East African Rift Zones
In addition to plate collisions, Morocco is near the western end of the East African Rift, a tectonic plate boundary where the African Plate is slowly splitting apart. This rift system can also produce earthquakes as the Earth’s crust is stretched and fractured.
Mediterranean Ridge
The Mediterranean Ridge is a complex geological feature in the Mediterranean Sea, and its interaction with the African Plate can lead to seismic activity in Morocco.
Subduction Zones
In the northwestern part of Morocco, the African Plate is subducting beneath the Eurasian Plate in the region known as the Alboran Sea. Subduction-related earthquakes can occur along this boundary.
Geography Plate Transform Faults
A transform fault, in the context of seismic activity and plate tectonics, is a type of fault that occurs at the boundary between two tectonic plates. Transform faults are characterized by horizontal motion along the fault plane, where the plates slide past each other horizontally in opposite directions. Unlike other types of plate boundaries, such as convergent boundaries (where plates move toward each other) or divergent boundaries (where plates move away from each other), transform boundaries involve plates moving horizontally past one another.
Transform faults, such as the North African Fault, play a role in the seismic activity of the region. These faults accommodate horizontal motion between the African and Eurasian Plates.
East African Rift Fault
Morocco also has several local fault systems that can generate earthquakes. The most well-known is the Rif Mountain Fault, which runs along the northern edge of the Rif Mountains.
Due to these geological factors, Morocco experiences a range of seismic events, from minor tremors to more significant earthquakes. As a result, earthquake preparedness and building construction standards are essential to mitigate the impact of seismic events on infrastructure and public safety in Morocco.



